About Pulse production
The production, marketing and consumption of nuts has grown tremendously in the last fifteen years. This report examines the processes and mechanisms of this growth, and the reasons behind them for different types of pulses. This report presents an analysis of the consumption patterns of pulses in different regions of the world and examines the potential role of pulses in human nutrition.
This report provides an overview of the growth of different vegetables in different countries. It explains the important role of trade in the global economy and provides an analysis of the evolution of trade. This report argues that there is an urgent need to close the large gap between potential and actual yields, particularly on smallholder farms in South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, by promoting good diversity and modern agricultural systems in all developing countries.
This, in turn, requires greater investment in agricultural research and expansion, access to better credit, and public investment focused on seed production. The report examines future prospects and policies necessary to support growth in pulse production.
Where does Pulses grow?
The Pulses is grown in almost all parts of the world. They have a strong history of feeding people around the world for centuries. Along with the first grains, seeds were among the first crops to be cultivated 11,000 years ago. Over the past three decades, world production of soybeans has increased rapidly.
In the last ten years alone, the world produces about 50 to 60 million tons of nuts per year. In 2015, the world’s largest producers of soybeans were India, Canada, Myanmar, China, Nigeria, Brazil, Australia, the United States, Russia and Tanzania, while the world’s largest exporters of soybeans included Argentina, France. , Ethiopia and Turkey.
In total, almost 173 countries around the world grew in the export of nuts between 2010 and 2013!
Areas, production and production
India is a producer (25% of world production), consumer (27% of world consumption) and importer (14%) of fruits in the world. Pulses constitute about 20% of the food sector and contribute about 7-10% of the total food consumption of the country. Although crops are grown during Kharif and Rabi seasons, Rabi crops contribute more than 60% of the total production.
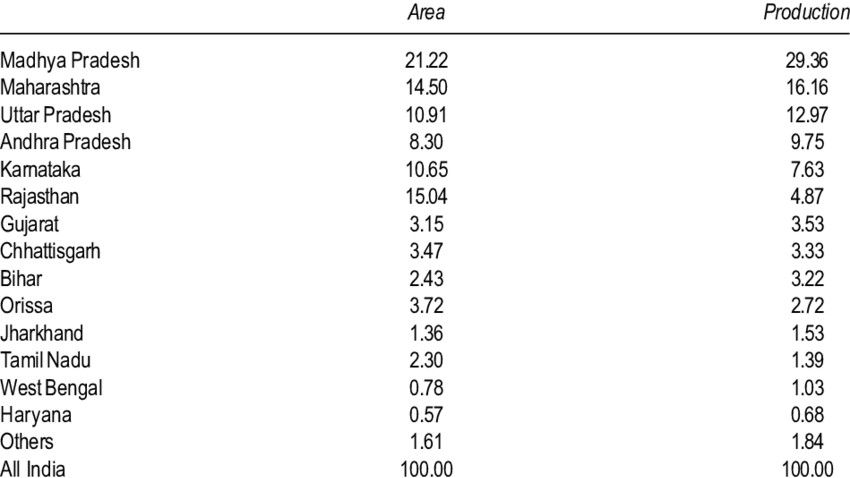
Gram is the dominant legume with a share of around 40% in total production, followed by Tur / Arhar at 15-20% and Urad / Black Matpe and Moong at around 8-10% each. Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh and Karnataka are the top five cashew producing states.
The productivity of beans is 764 kg/ha. Over the years, soybeans have successfully entered the agricultural system of our country because farmers can use their own seeds and family labor to produce them without depending on external input. With the advent of the green revolution, which improved rice and wheat using external inputs and modern seed varieties, the seeds were moved to neighboring lands.
This has led to productivity and land degradation. As a result, crops are still grown in the soil and subsoil areas, especially under rainfed conditions. This process of commercialization of agriculture has worsened the condition of seeds in the agricultural system.
Global Productivity of Pulses
In 2018, the last year for which we have official production figures, the world produced about 92.4 million tons. Between 1998 and 2018, soybean production increased by nearly 36 million metric tons (or 63%). This compares to an increase of only 12.5 million metric tons between 1978 and 1998.
The expansion of seed production in the last two decades is particularly interesting, not least because it has expanded all crops in the producing areas. A significant increase was achieved in the production of common beans (+14 million MT), chickpeas (+8.3 million MT), lentils and pigeon peas (+3.6 million MT each), cowpeas (+3.5 million MT) and dry peas (+ 1.2). million tons). In terms of regions, production increased by 17.3 million tons in Asia (South Asia contributes 12 million tons to this total), by 10.5 million in Sub-Saharan Africa, by 4.8 million tons in North America and 2.2 million tonnes in Latin America and the Caribbean.
Top Countries for Pulses Production
India

When it comes to production and consumption of pulses, no other country comes close to India. In the last two decades, India has increased the production of sugarcane, while the minimum production of the last two decades was recorded in 2002, around 11.13 million metric tons.
In the current fiscal year, the production of sugarcane is on the rise with 26.96 million metric tons in one year. Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh are the top cashew producing states in India.
Bengal gram, pigeon peas, black eyed peas, black matpe, green beans, chickpeas, kidney beans, lentils and white peas are widely produced in India. And if you live in India, you probably eat most or all of these things before.
Myanmar
In 2020-2021, Myanmar exported more than 2 million tons to other countries that have a great demand for these grains. Well, you will be surprised to know the total number of production in Myanmar since the production sector is high in this country.
At first glance, Myanmar is a small country compared to other major producers, but despite that, in 2021, it managed to produce more than 7 million metric tons. For FY2022, Myanmar is expected to cross the 7.4-7.5 million ton mark.
Benefits of Pulses
Pulses are rich in nutritional value and protein and are an important part of a healthy diet.
Grains and legumes (lentils, peas, chickpeas, beans, soybeans and peanuts) also play an important role in maintaining health and improving overall health. Pulses are also key contributors to achieving the goals of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
Pulses play an important role in addressing the challenges of poverty, food security, poor health and climate change. Fruits and vegetables help improve the efficiency of the agricultural production process.
Pulses contribute to environmental benefits. The nitrogen-fixing properties of hemp improve the fertility of the soil, which increases the production and productivity of the agricultural land.
Pulses are important for good nutrition.

